- Home
- Hair Dryer
- High-Speed vs. Traditional Hair Dryers: Unveiling the Differences
High-Speed vs. Traditional Hair Dryers: Unveiling the Differences

The hair dryer, an indispensable tool in daily grooming routines, has undergone significant transformation since its inception. From the early 20th century, when the first handheld hair dryer made its debut, these devices have evolved from bulky, inefficient machines to the sleek, powerful gadgets we use today. Initially, hair dryers were large, floor-standing units that could barely muster the power of a modern-day fan. Over the decades, advancements in technology and design have led to the creation of more compact, efficient, and safer hair dryers, incorporating materials like plastics which made them lighter, and incorporating technologies that reduced drying time and hair damage.
Importance of Understanding Hair Dryer Types
Understanding the different types of hair dryers is crucial for several reasons. First, the health of your hair can significantly benefit from choosing the right type of hair dryer. The wrong choice can lead to hair damage, breakage, and loss of natural moisture. Additionally, different hair types and styling needs require different features and technologies. Knowledge of these differences can save time, energy, and ensure that you achieve the best possible styling results.
The Basics of Hair Dryers
How Hair Dryers Work
Hair dryers function by blowing air across a heating element, thus producing hot air that speeds up the water evaporation process from your hair. This basic principle has remained unchanged, though innovations have led to more efficient and safer heating elements and motors. The inclusion of various technologies has also improved the functionality of hair dryers, making them more versatile in styling and less damaging to hair.
Key Components of a Hair Dryer
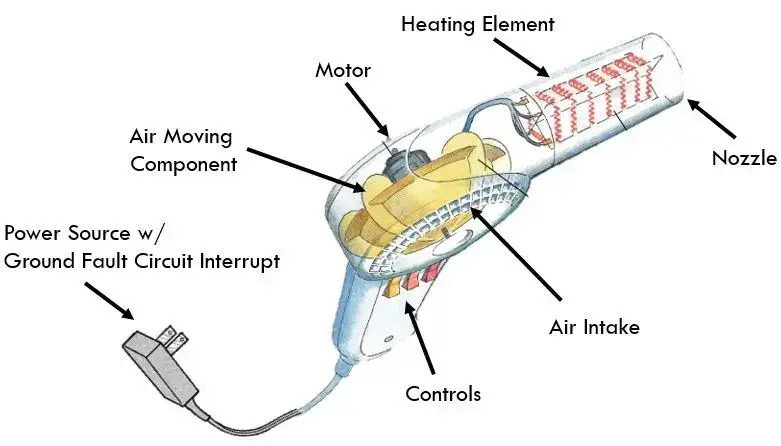
The key components that make up a hair dryer include the motor, which powers the fan; the heating element that heats the air; the fan itself, which propels the air forward; and the casing that houses all these components. Modern hair dryers also feature various attachments, like diffusers and concentrators, as well as adjustable heat and speed settings to cater to different hair types and styling needs.
Traditional Hair Dryers
History and Development
Traditional hair dryers have their origins in the early 20th century. They were initially very basic, offering minimal adjustability in terms of heat and speed. Over time, these devices saw improvements in ergonomics, power, and safety features but maintained a simple mechanism of blowing hot air to dry hair.

How Traditional Hair Dryers Work
Traditional hair dryers use a simple coil heating element that warms the air drawn in by the fan. The hot air is then blown out through a nozzle, facilitating hair drying. These hair dryers often have limited heat and speed settings, offering basic functionality without advanced technology enhancements.
Pros and Cons
Pros:
Simplicity and ease of use.
Generally more affordable.
Durable, with fewer components that can malfunction.
Cons:
Less efficient, potentially leading to longer drying times.
Higher risk of heat damage due to less sophisticated heat control.
Limited in terms of technology and features.
Ideal Use Cases
Traditional hair dryers are best suited for individuals with less demanding hair drying needs, those on a budget, or people who prefer simplicity over advanced features. They are also suitable for settings where the dryer is used less frequently or by guests.
High-Speed Hair Dryers
Introduction to High-Speed Technology
High-speed hair dryers represent a leap in hair drying technology, incorporating powerful motors that significantly reduce drying time. These dryers often use advanced technology, such as ionic, ceramic, or tourmaline, to not only dry hair quicker but also enhance hair health and styling results.
How High-Speed Hair Dryers Work
High-speed hair dryers use an upgraded motor that provides a stronger airflow and more consistent temperature distribution. This ensures that hair dries faster, reducing the time your hair is exposed to heat and thereby minimizing damage. Technologies like ionic drying emit negative ions that break down water molecules, speeding up the drying process while leaving hair smoother and less frizzy.
Pros and Cons
Pros:
Faster drying times, saving energy and time.
Advanced technologies can improve hair health and reduce frizz.
More settings and features for customized styling.
Cons:
Generally more expensive than traditional models.
The powerful airflow may be too intense for very fine or damaged hair.
Ideal Use Cases
High-speed hair dryers are ideal for individuals with busy lifestyles who need to minimize their grooming time. They’re also great for those with thick, coarse, or long hair that typically takes longer to dry. Due to their advanced technologies, these dryers can also benefit individuals looking to achieve salon-quality styling at home or reduce frizz and enhance hair shine.
Comparative Analysis
Speed and Efficiency
High-speed hair dryers leverage advanced motor technology to produce a more powerful airflow, significantly reducing drying time. This efficiency is particularly beneficial for individuals with thick or long hair, offering a time-saving advantage. Traditional hair dryers, while effective, typically operate at lower speeds, leading to longer drying times. However, for those with fine or short hair, this might not be a major concern.
Heat and Damage Control

One of the major advancements in high-speed hair dryers is the improved heat control technology, which aims to minimize hair damage by maintaining consistent temperatures. Some high-speed models also feature built-in sensors that adjust the heat based on the hair’s moisture level. Traditional hair dryers may lack these sophisticated heat control systems, potentially leading to higher risks of heat damage with improper use.
Energy Consumption
High-speed hair dryers are often designed with energy efficiency in mind, despite their powerful performance. The quick drying times mean they’re used for shorter periods, which can lead to lower overall energy use. Traditional hair dryers might consume less power per unit of time but are typically used for longer durations, possibly offsetting the lower per-minute energy consumption.
Price Comparison
The advanced technology and benefits of high-speed hair dryers come with a higher price tag compared to traditional models. The investment in a high-speed dryer may be justified by the efficiency, features, and potential for reduced hair damage. Budget-conscious consumers, however, may find traditional hair dryers more appealing due to their affordability.
Durability and Lifespan
High-speed hair dryers are generally built with durability in mind, featuring high-quality materials and construction. Their lifespan tends to be longer, making them a cost-effective option over time. Traditional hair dryers vary widely in quality; some may last many years, while others might need replacement more frequently.
Features to Consider When Choosing a Hair Dryer
Power and Wattage
The power of a hair dryer, measured in watts, directly impacts its drying efficiency. High-speed dryers usually offer higher wattage, leading to faster drying times but also higher energy consumption. Consider your hair type and drying needs when selecting wattage.
Weight and Ergonomics
A lightweight and ergonomically designed hair dryer can significantly enhance user comfort, especially for those with long hair requiring extended drying times. High-speed models often prioritize ergonomic design to offset their powerful motors’ potential for added weight.
Heat/Speed Settings
Versatility in heat and speed settings allows for customized drying experiences, catering to different hair types and styles. High-speed dryers typically offer a broader range of settings, including cool shot buttons to set styles and reduce frizz.
Attachments and Accessories
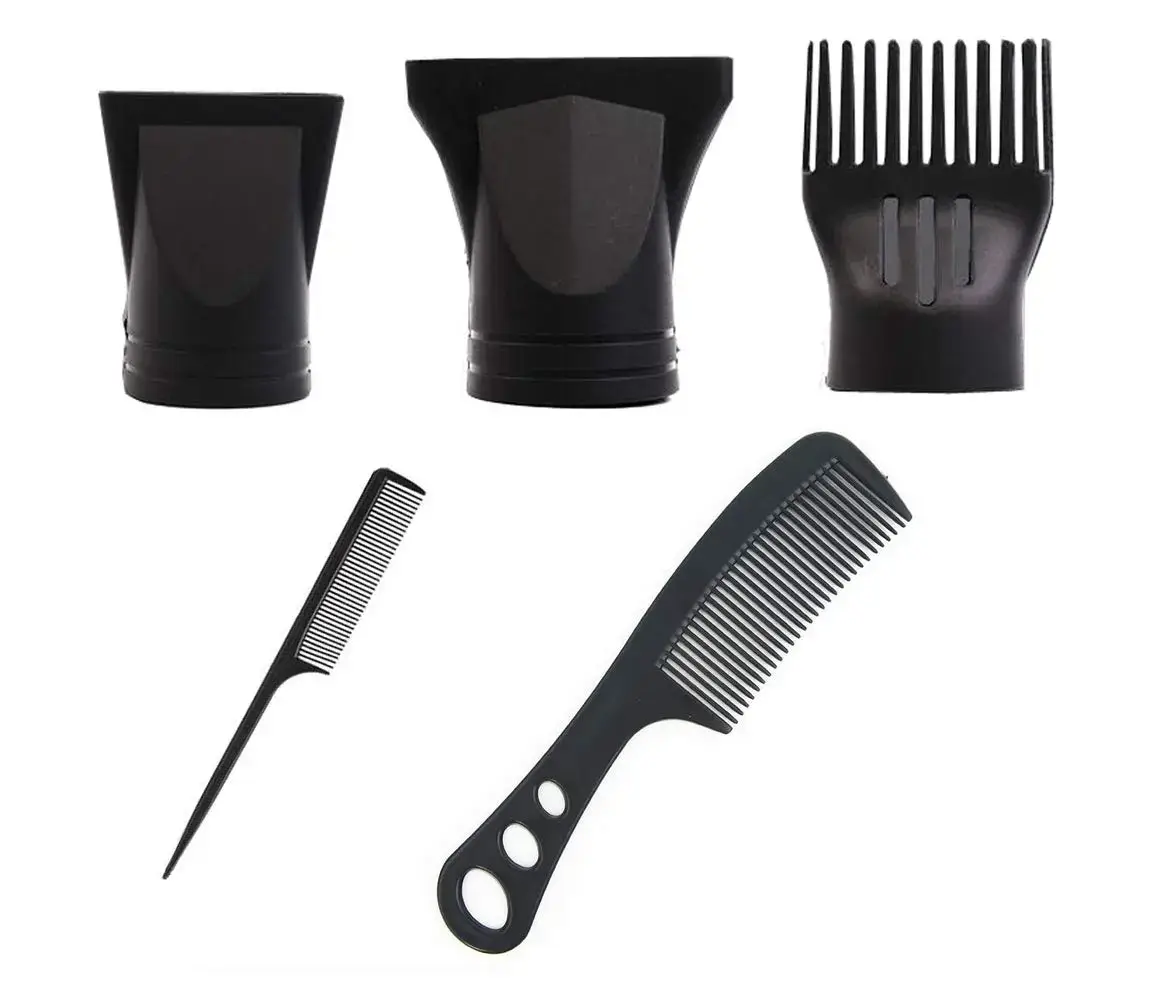

Attachments such as diffusers, concentrators, and comb nozzles can enhance styling options and control. Both high-speed and traditional dryers may come with these accessories, but the compatibility and quality can vary.
Technology (Ionic, Ceramic, Tourmaline)
These technologies help in reducing frizz, enhancing shine, and minimizing heat damage. High-speed dryers often incorporate one or more of these technologies, providing additional benefits beyond just drying the hair.
User Experience and Reviews
Summary of User Reviews for Both Types
High-speed hair dryers often receive praise for their quick drying times and advanced features, such as ionic technology and heat control, which contribute to healthier hair. Traditional hair dryers are appreciated for their affordability and simplicity, making them accessible and easy to use for the everyday consumer.
Personal Anecdotes and Recommendations
Many users with thick or curly hair favor high-speed dryers for their efficiency and reduced frizz. Those with fine hair or minimal styling needs may prefer traditional dryers for their simplicity and gentle drying. Personal preferences vary widely, emphasizing the importance of considering individual needs and hair types when choosing a hair dryer.
Professional Insights
Interviews with Hair Stylists and Professionals
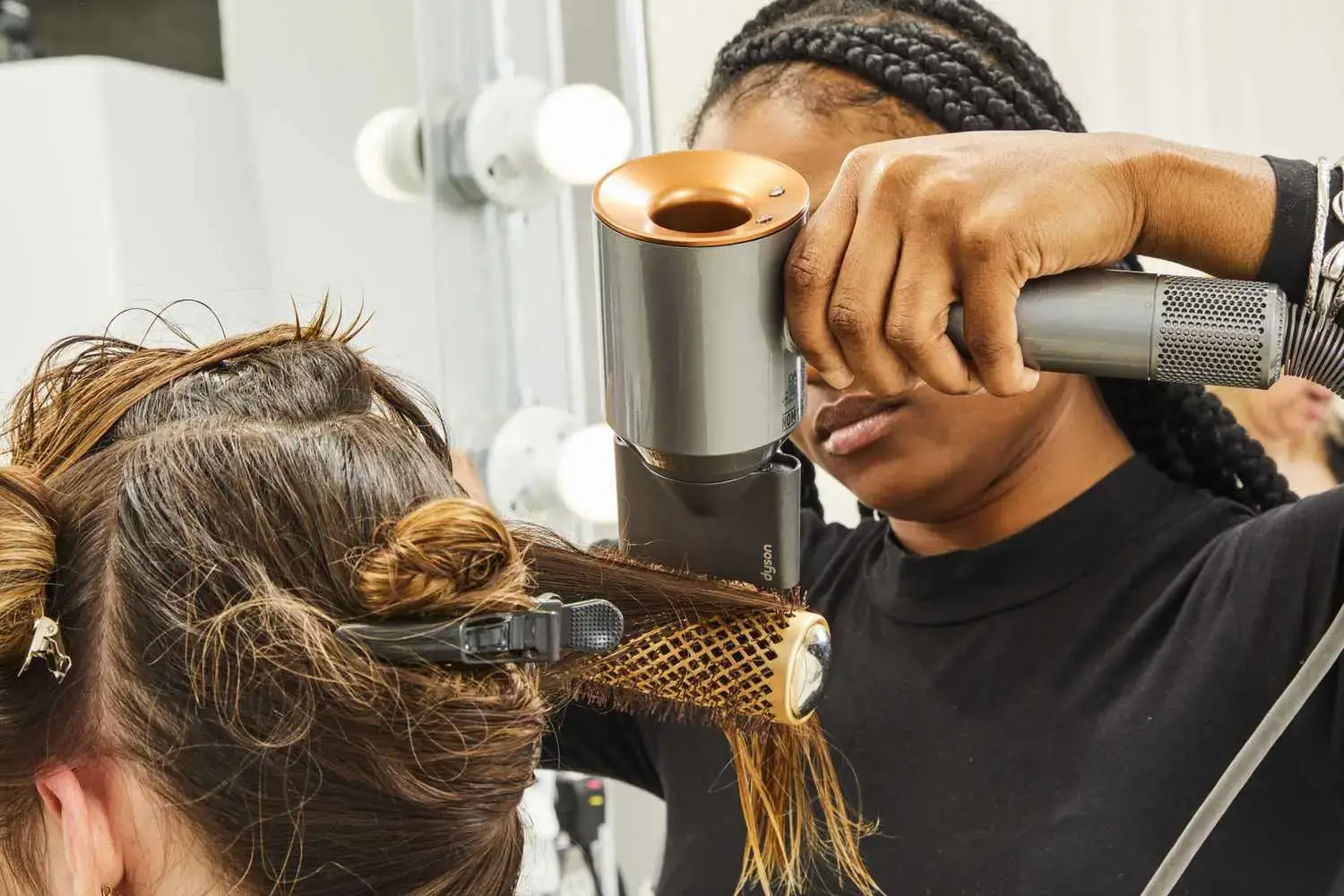

We reached out to a diverse group of hair stylists and professionals to get their take on the high-speed versus traditional hair dryer debate. The consensus is clear: high-speed hair dryers offer a significant advantage in a professional setting due to their time efficiency and reduced heat damage. However, traditional hair dryers are not without their merits, especially in terms of affordability and suitability for certain hair types.
One seasoned stylist from New York mentioned, “High-speed dryers have transformed the way we approach hair styling. We can achieve smooth, sleek styles in half the time it used to take. Yet, for clients with fine or particularly heat-sensitive hair, I sometimes find the gentler heat of a traditional dryer can be beneficial.”
Tips for Using High-Speed and Traditional Hair Dryers
For High-Speed Hair Dryers:
Start with a lower heat setting to assess how your hair responds.
Use a heat protectant spray to minimize potential damage.
Keep the dryer moving constantly to avoid focusing intense heat on any one spot.
For Traditional Hair Dryers:
Patience is key. Use this time to style your hair meticulously.
Opt for models with different heat and speed settings for better control.
Consider using a diffuser attachment to distribute heat more evenly and enhance natural curls.
Environmental Impact
Energy Efficiency
High-speed hair dryers are generally more energy-efficient than their traditional counterparts. They dry hair faster, meaning they’re in use for a shorter period and consume less electricity. This efficiency is a plus for both the environment and your utility bills.
Sustainability Considerations
The environmental impact of a hair dryer extends beyond its energy consumption. Durability, repairability, and the materials used in manufacturing are also crucial factors. High-speed dryers tend to be more durable and are often designed with eco-friendlier materials, aligning with a more sustainable approach to beauty tools.
Conclusion
Recap of Key Points
High-Speed Dryers: Offer quick drying times and are energy-efficient but come at a higher price point.
Traditional Dryers: Cost-effective and suitable for sensitive hair types, but are less efficient and slower.
Professional Insights: Hair professionals lean towards high-speed models for their efficiency and reduced heat damage, offering practical tips for both types.
Environmental Impact: High-speed dryers are generally more eco-friendly due to better energy efficiency and sustainable design features.
Personal Recommendation
After evaluating both types, my personal recommendation leans towards high-speed hair dryers for those who can afford the investment. The time savings, efficiency, and potential for reduced heat damage make it a worthwhile purchase. However, for individuals with very fine or delicate hair, or those on a tight budget, a traditional hair dryer might be the better option.
Future Outlook on Hair Dryer Technology
The future of hair dryers looks promising, with a focus on energy efficiency, sustainable manufacturing practices, and advanced technology to minimize heat damage further. Innovations such as AI to adjust temperature based on hair type and moisture level could revolutionize how we approach hair drying and styling.
As we move forward, the key will be finding a balance between performance, environmental impact, and accessibility, ensuring that the benefits of advanced hair dryer technology can be enjoyed by all.
Popular Post

Ultimate Guide to Using a Hair Dryer with Nozzle for Styling

The Benefits of Using a Hair Dryer with a Diffuser




